Logic gates serve as the essential components of digital electronics. They execute fundamental logical operations that are crucial for digital computing. Logic gates take binary inputs (0s and 1s) and generate a binary output according to specific logic rules. These gates are constructed using electronic switches, such as transistors, and constitute the foundation of digital systems, including computers, calculators, and digital signal processors.

The notion of logic gates originates from Boolean algebra, a mathematical field that focuses on true/false values. In the realm of digital electronics, the binary digits 0 and 1 symbolize false and true, respectively.
Fundamental Logic Gates
There exist three main logic gates: AND, OR, and NOT. These serve as the basis from which all other gates are derived. Logic gates are an important concept if you are studying electronics. These are important digital devices that are mainly based on the Boolean function. Logic gates are used to carry out logical operations on single or multiple binary inputs and give one binary output. In simple terms, logic gates are the electronic circuits in a digital system.
AND Gate
The AND gate accepts two or more inputs and generates an output of 1 solely when all inputs are 1. If any input is 0, the output will be 0.
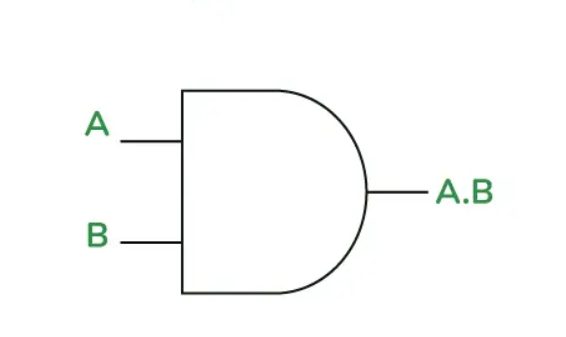
A | B | A AND B |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
OR Gate
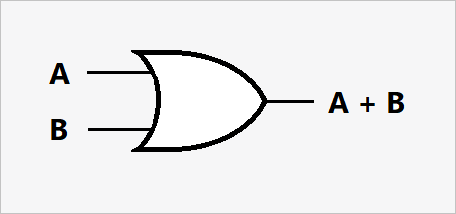
The OR gate is designed with two or more inputs and produces an output of 1 if at least one of the inputs is 1. The output will be 0 only when all inputs are 0.
A | B | A OR B |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
NOT Gate
The NOT gate functions as a single-input gate that reverses the input signal. When the input is 0, the output becomes 1; conversely, when the input is 1, the output changes to 0.
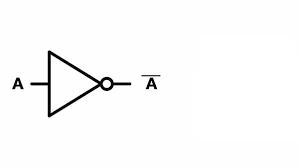
| A | NOT A |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
Universal Gates
The NAND and NOR gates are referred to as universal gates since it is possible to create any other type of gate (such as AND, OR, NOT, XOR, etc.) using only NAND or NOR gates.
NAND Gate
The NAND (Not AND) gate serves as the inverse of the AND gate. It produces an output of 0 exclusively when all inputs are 1.
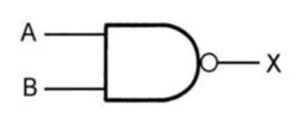
| A | B | A NAND B |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
NOR Gate
The NOR (Not OR) gate serves as the inverse of the OR gate. It produces an output of 1 exclusively when all inputs are 0.
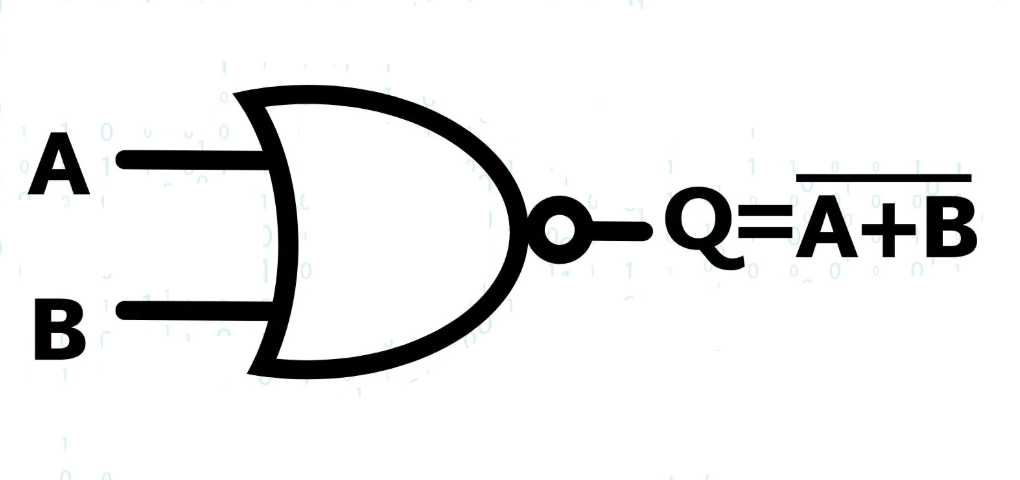
| A | B | A NOR B |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Other Significant Gates
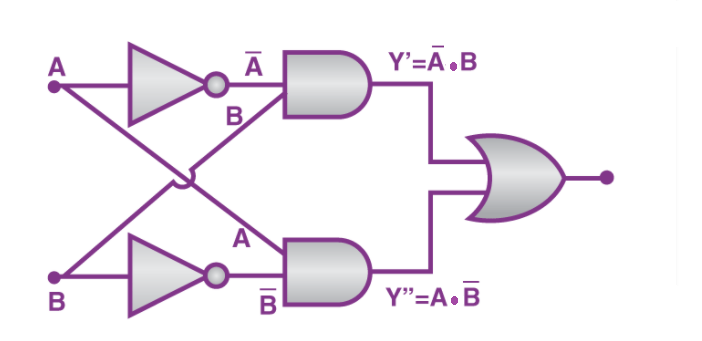
XOR Gate (Exclusive OR)
The XOR gate produces an output of 1 solely when the inputs differ. It is utilized in circuits that carry out addition and comparison.
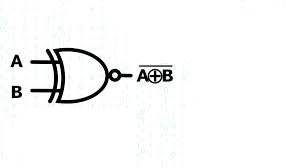
| A | B | A XOR B |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
XNOR gate
The XNOR gate serves as the inverse of the XOR gate. It produces an output of 1 when the inputs are identical.
| A | B | A XNOR B |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Applications of Logic Gates
Logic gates are integral to nearly every digital device. Below are several typical applications:
Arithmetic Circuits: Adders, subtractions, and multipliers all utilize logic gates for numerical processing.
Decision Making Circuits: Microcontrollers and processors employ logic gates to facilitate decision-making and manage program flow.
Memory Devices: Flip-flops and latches, which are essential for data storage in computers, are constructed using logic gates.
Signal Processing: Logic gates are employed to filter and convert signals within communication systems.
Security Systems: AND and OR gates are utilized in alarm systems to establish access conditions.
Conclusion
Logic gates serve as the fundamental building blocks of all digital electronics. They enable computers and various digital systems to execute functions such as addition, comparison, memory storage, and decision-making. Grasping their operation is crucial for anyone pursuing interests in electronics, computer science, or engineering. From basic home electronics to intricate processors in supercomputers, logic gates facilitate it all.