Additionally, application software can be categorized based on its cost and accessibility. Examples of application software include the following:
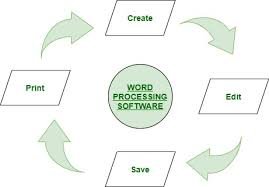
1. Software for word processing: Word processing is the process of creating, editing, saving, and printing documents on a personal computer (PC) or laptop. This can only be done with specialist software called a word processor. All professionals use Microsoft Word, which is an example of a word processor.
2. Spreadsheet programs: Through an automated version of an accounting worksheet, spreadsheet software is a kind of computer program that allows a user to study numbers and perform numerical operations. Microsoft Excel is the best example of spreadsheet software.

3. Software for presentations: A specific type of application program called presentation software, also referred to as presentation graphics, is used to create word and picture sequences that tell a story, support a speech or public presentation of any kind of information, or announce the launch of new goods or services.

4. Software for Multimedia: Combining text, audio, graphics, animation, and video to create a variety of interactive content for both personal and commercial usage is known as multimedia software. Learning about file formats, media players, and the general operation of audio and video software is simple.
5. Internet browsers: You can explore the entire internet with a web browser. It pulls information from other websites and displays it for you to view on your desktop or mobile device. The Hypertext Transfer Protocol, which outlines the sharing of text, images, and video on the World Wide Web, is used to transfer the data.

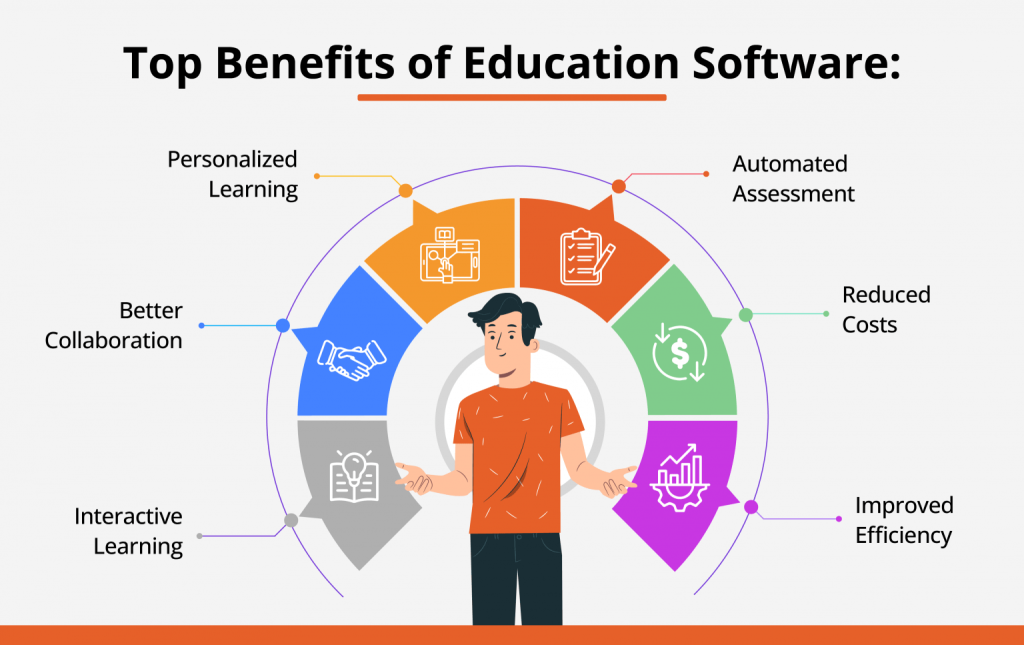
6. Educational Software: Educational software refers to any computer software designed solely for educational reasons. It includes a wide range of software, including language learning software, classroom management software (CMS), and reference software for students and other professionals.
7. Graphics Software: Graphics software can rework with bitmap and/or vector graphics and can be utilized to create label templates. Graphics software generally includes Canva, Adobe Illustrator, Photoshop, InDesign, CorelDRAW, Inkscape, Microsoft Paint, and Paint.NET.

8. Freeware: Freeware is typically marketed for profit but might be allocated specifically for a business or commercial purpose with the aim of expanding the market share of any newly launched premium product. Some of the widespread examples of closed-source freeware include Adobe Reader, Free Studio, and Skype.

9. Shareware: Shareware is software that is given away for free during a trial period so that users can test or use it for a set number of days. If they are happy with the program’s functionality, they may decide to purchase it later. There are software companies that offer shareware versions of their products that have an expiration date built in. This means that the customer or user will no longer be able to access the application after 30 days.
10. Software for Simulation: By simulating real-world occurrences in a computer-generated environment, simulation software enables engineers to assess, optimize, and compare product designs with those of other comparable software.
10. Open Source: Open source software is a particular type of code that is made to be publicly available, allowing everyone to see, alter, and share the code as they see appropriate. Its decentralized and coordinated design relies on community production and peer evaluation.

12. Source Closed : Software that does not make its source code publicly available is known as closed source software. It is created and sent to the client as an executable collection of files that have been fully complied. After a purchase, the developer frequently helps users and makes sure the program functions as intended.
Benefits of Application Software
- It satisfies the unique needs and expectations of each client. Because the task is explicitly defined for a single purpose, the client typically understands that they must use only one explicit program to do it.
- Companies that deal with particular applications can limit access and consider ways to keep an eye on their operations.
- General logic of health can be used to get standard updates from engineers for licensed application programming.
Application software drawbacks
- It can be expensive for developers to create and modify application software to accomplish particular objectives, but this can have a significant effect on their budget and revenue stream, especially if an excessive amount of time is invested in a product that isn’t often worth.
- Application software that is used by a large number of people and subsequently shared online is prone to infection by bugs or other malicious activities.
The distinction between application and system software
While Microsoft Office, Photoshop, and CorelDRAW are well-known examples of application software, the Windows operating system is a great example of system software.
System Software | Application Software |
| The main purpose of this software is to manage the resources available in the system. It serves as an effective forum for the execution of application software | Application software is designed to achieve a certain set of tasks. |
| System software is documented in a low-level programming language like machine code or assembly language. | Application software is composed in a high-level language like Java, C++, .NET, or PHP. |
| Usually, when the computer is switched on, system software begins to run and stops when the computer is switched off. | When a user requests, application software runs according to the task it is assigned. |
| Without system software, a computer system cannot even activate. | User-specific application software is definitely not required to run the system. |
| The system software has a wide scope of capabilities. | The objective of the application software is to achieve or perform a certain task. |
| System software comprises language processors (interpreters, compilers, and assemblers), operating systems, and so on. | Payroll software, accounting software, MS Office, and so on are perfect examples of application software. |
