Business application software can be categorized according to its cost and how its final users use it. The following software is a business application:
Relationship Management for Customers (CRM)
A tool called customer relationship management (CRM) keeps track of all of your business’s contacts and transactions with current and potential clients. Strengthening business relationships is the ultimate objective. Businesses can boost income, streamline processes, and maintain a relationship with their customers by implementing a CRM system.
Role of CRM
- It sets bold aspirations, i.e, a clear vision for the development of the relationship.
- It sets and executes the client relationship strategy.
- It creates, manages, and leads the team.

Functions of CRM
- Acquiring and storing information.
- Increase sales.
- Improve quality.
- Customer Management.
- Proper communication network.
Advantages of CRM
- Customers are motivated to return again and again as they receive good customer service and continue to do business.
- It enables an organization to create detailed profiles, such as customer likes/dislikes.
- It decreases the cost.
- It highlights the poor operational processes.
- It increased access to a source of market and competitor information.
Disadvantages of CRM
- Security and privacy in the cloud.
- Limited control and flexibility.
- Increased vulnerability.
- It needs additional management to maintain.
- It may result in duplication of tasks.
Planning for Enterprise Resources (ERP)
The software that a business uses to manage important aspects of operations, such as accounting and resource management, is called enterprise resource planning, or ERP.
Benefits of ERPs
Here are the key benefits of implementing the ERP systems:
- Improved Efficiency: ERP systems reduce the manual effort and risk of errors by automating repetitive processes.
- Integrated Business Processes: ERP systems streamline operations by integrating various business processes and enabling seamless data flow across the departments.
- Reduced Redundancy: ERP systems eliminate duplicate data entries and improve data integrity.
- Timely Data Access: ERP systems provide real-time data access, thus helping in making timely and informed decisions.

Weaknesses of ERPs
ERP systems offer numerous benefits, but they also come with several weaknesses and challenges. Here are some of the weaknesses of ERP systems:
- High Implementation Costs: Implementing an ERP system can be expensive and time-consuming. It requires significant investment in hardware, software, and personnel, as well as training and consulting costs.
- Complex Customization: Customizing an ERP system to meet the specific needs of an organization can be complex and require specialized knowledge. This can lead to delays and additional costs.
- Resistance to Change: ERP systems often require significant changes to an organization’s processes and workflows, which can be met with resistance from employees who are comfortable with existing practices.
- Data Security Risks: Centralizing sensitive business data in an ERP system creates potential security risks, especially if the system is not properly secured or if there are vulnerabilities in the software.
Software for Project Management
Project planning, scheduling, resource allocation, and change management are the primary functions of project management software. It enables project managers (PMs) to efficiently oversee and manage every official job from a single location.
Database
An automated data-keeping system is essentially what a database management system (DBMS) is. In order to do different kinds of operations on the system, such as database structure management or data modification in the database, users are given specialized structures.
Management of Business Processes
In general, business process management software (BPMS) is an enterprise-level software program designed to automate repetitive processes, control basic processing, and manage particular technique logic. BPM systems increase efficiency by streamlining and optimizing processes.
Advantages of BPM:
1) Enhanced Efficiency: Productivity is raised and waste is decreased through streamlined procedures.
2) Decreased Costs: Operational costs are decreased by automation and improved procedures.
3) Better Customer Experience: Faster service, fewer mistakes, and higher satisfaction are all results of improved processes.
4) Enhanced Agility: BPM assists businesses in adjusting to shifting consumer demands and market situations.
5) Improved Decision Making: BPM’s data-driven insights help make well-informed choices.
BPM types include:
- Connecting several software systems (such as CRM and ERP) is known as integration-centric BPM.
- Process management focused on papers, such as contracts, is known as document-centric BPM.
- Human-centric BPM: Emphasizing how people work together and interact with processes.
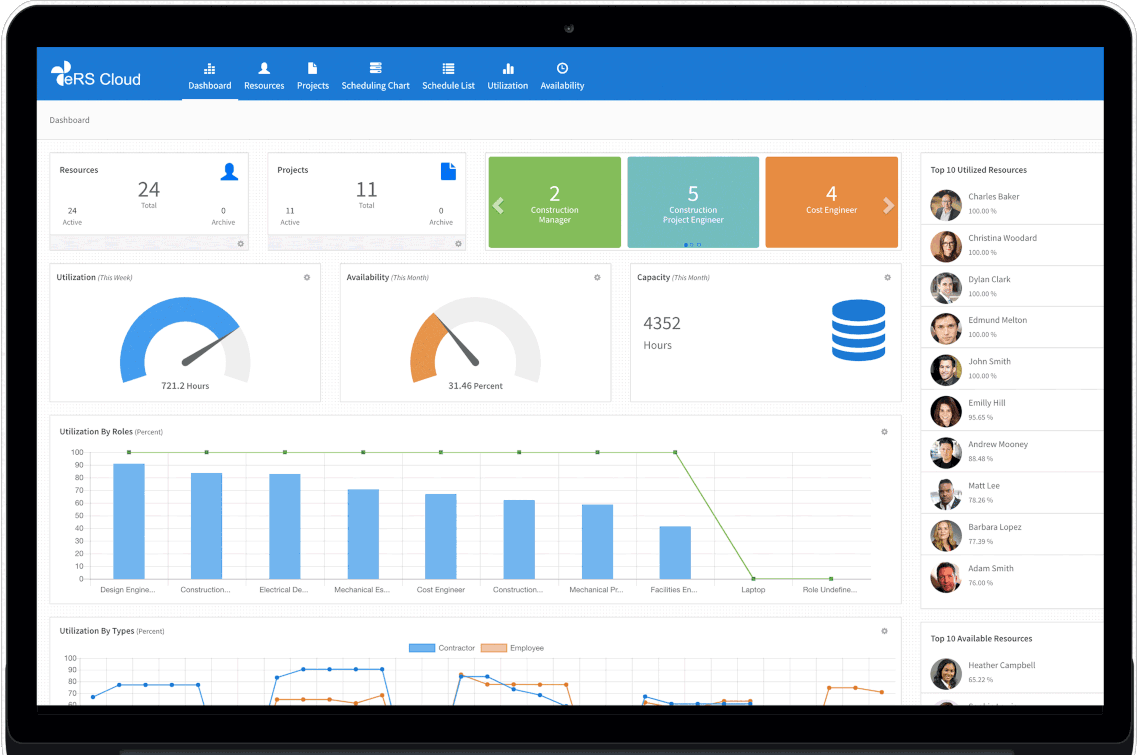
Software for Resource Management
Resource management software, often known as resource planning software, is a tool used to manage an organization’s program and human resources. When necessary, a resource planning system will assist you in assigning personnel to projects.
Educational Software
Educational software involves any computer application that improves the learning process. It possesses classroom management software, student information systems, language software, reference software, and even more.
Software for Productivity
One type of application program that enables end users to create documents, databases, spreadsheets, graphs, and presentations is called productivity software. By reducing people’s workloads, productivity software boosts an organization’s efficiency.

Personalized Software
The process of designing, creating, and manufacturing specialized software applications is known as custom software development. These software programs are designed for certain people, processes, and business needs.